Statistics for African collections at the Pitt Rivers Museum up to 1945 Part I
1. What was colonial history of geographical area
[article ID:198]
Anglo-Egyptian Sudan
1820 – governed by Egypt
*1898 – British victory in invasion wars
1899 – Anglo-Egyptian Condominium set up and area effectively becomes British Protectorate
1955 – independence as Sudan
Basutoland
*1865 – protectorate established
1871 – annexed to Cape Colony
1884 – comes under direct control from UK
1910 – on South Africa s independence, Basutoland remains British and under jurisdiction of British High Commissioner in South Africa
(much reluctance in Basutoland to become part of South Africa)
1966 – independence as Lesotho
Bechuanaland
*1884 – established as a Protectorate
[1895 – southern part incorporated into Cape Colony]
1966 – independence as Botswana
British Cameroons
*1919 – Britain administers smaller western parts of Kamerun (France has the rest), dividing it into Southern and Northern Cameroons
1961 – Northern Cameroons join Nigeria; Southern Cameroons become fully independent with former French territories as Cameroons Republic [note 80% of this country is formerly French, and 20% formerly British]
British Somaliland see below
Cape Colony
*1814 – created
1910 – merged into Union of South Africa as Province of Cape of Good Hope
Egypt
some sources say never considered part of British Empire, but:
*1882 – comes under British control
1914 – formally becomes a British Protectorate 1914
1922 – independence
Eritrea
*1941 – becomes British (gained from Italy)
1952 – passes back to Italy
[1962 – becomes part of independent Ethiopia
1993 – independence as Eritrea]
The Gambia
1618 – first settlements
*1843 – becomes a Crown Colony
1965 – independence
The Gold Coast
1618 – first settlements
*1821 – Direct Rule begins
1957 – independence as Ghana
Kenya *
1888 – British begin to settle area (1505-1729, Portuguese settlements)
1895 – East Africa Protectorate declared
1920 – becomes a Crown Colony
1963 – independence
Mauritius
[1511 – Portuguese; 17th century – Dutch; 1715 – French]
*1814 – becomes British
1968 – independence
Natal
*1844 – annexed to Cape Colony
1856 – becomes a separate colony
1910 – merged into Union of South Africa
Nigeria
before 1851 – area under spreading influence of National Africa Company
*1851 – Lagos seized by British
1886 – region becomes a British colony (and National Africa Company changes its name to Royal Niger Company)
1914 – area now recognised as Nigeria is formed
1954 – Eastern, Western and Northern regions organised into a unified state
1956 – Eastern and Western regions gain internal self-government
1960 – independence
1963 – declares itself a Republic
Northern Rhodesia *
1889 – controlled, together with Southern Rhodesia, by Rhodes' South African Company
1911 – split administratively from Southern Rhodesia (border = Zambezi)
1924 – South African Company control ends and area becomes a Crown Protectorate
1953 – briefly rejoined by Welensky with Southern Rhodesia and with Nyasaland to form Central African Federation
1963 – Central African Federation dissolved
1964 – independence as Zambia
Nyasaland
*1891 – becomes a British Protectorate
1953 – briefly joined by Welensky with Southern Rhodesia and with Northern Rhodesia to form Central African Federation
1960 – leaves Central African Federation
1964 – independence as Malawi
Orange Free State *
1848 – annexed to Empire but then Boers (who were already there) were allowed to develop their own Free State
1854 – Boers free state confirmed by Bloemfontein Convention
1900 – overrun by British in Anglo-Boer War and annexed as Orange River Colony
1910 – merged into Union of South Africa
Sierra Leone *1788 – first settlements
1808 – becomes a Crown Colony
1961 – independence
Seychelles
[1756 – French]
*1794 – British capture them and they become a dependency of Mauritius
1904 – become a Crown Colony separate from Mauritius
1976 – independence
Somaliland
1887 – part of what is now Somalia becomes the protectorate of British Somaliland; rest of what is now Somalia is at this time Italian
Somaliland
1941 – Britain gains Italian Somaliland
1950 – Italian Somaliland passes back to Italy
1960 – both British and Italian Somalilands become independent and join up as United Republic of Somalia
[note that what was once French Somaliland is now the separate country of Djibouti]
Southern Rhodesia
*1889 – controlled, together with Northern Rhodesia, by Rhodes' South African Company
1911 – split administratively from Northern Rhodesia (border = Zambezi)
1924 – South African Company control ends and area becomes a Crown Colony
1953 – briefly rejoined by Welensky with Northern Rhodesia and with Nyasaland to form Central African Federation
1963 – Central African Federation dissolved
1964 – Ian Smith becomes premier and declares unilateral independence
1970 – Smith declares Rhodesia a republic
1980 – Mugabe becomes President of what is now Zimbabwe
[South West Africa technically never part of British Empire – first German, then South African – by the time the colony passed to South Africa, the latter country had Dominion Status and so was effectively independent, although this was not formally established by UK Parliament until 1931
[1880-1915 – German Protectorate of South West Africa]
1915 – captured by Allies
1919 – becomes South African mandate
1990 – independence (from South Africa) as Namibia]
St Helena
*1659 – controlled by East India Company
1815 – leased to British government (as prison for Napoleon)
1834 – becomes Crown Colony; still an overseas territory
Swaziland
*1894 – becomes protectorate of the Transvaal
1910 – included in Union of South Africa as South-Eastern Transvaal
1968 – independence as Swaziland
Tanganyika
[1885 – German East Africa established]
*1919 – small part goes to Belgium (Rwanda and Burundi) and Portugal; rest becomes British mandated Tanganyika Territory
1961 – independence
1964 – Zanzibar joins, and country is renamed Tanzania
Togoland
*1914 – gained from Germany by French and British forces; Western Togoland becomes British Togoland and is administered from Gold Coast (the rest becomes French Togoland and eventually becomes independent as the Republic of Togo)
1957 – British Togoland gains independence as region of Ghana
Transvaal
1836/7 – Boers establish independent republic after Great Trek
*1877 – British annex region
1881 – Boers granted independence
1900 – falls again to British
1910 – becomes province of Union of South Africa
Uganda
*1884 – Lugard arrives in area
1894 – British protectorate declared
1961 – internal self-government granted
1962 – independence
Zanzibar
*1890 – becomes a British Protectorate
1963 – independence
1964 – becomes part of Tanzania
Non-British Colonies or always independent countries [Africa]
Algeria
Angola
Benin Republic
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cameroon Cameroun
Cape Verde
Central African Republic
Chad
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of
Congo, People's Republic of
Côte d'Ivoire Ivory Coast
Djibouti
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Ethiopia
Gabon
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Liberia
Libya
Madagascar
[Madeira]
Mali
Mauritania
Mayotte
Melilla
Morocco
Mozambique (Moçambique)
Niger
Reunion
Rwanda
São Tomé & Príncipe
Senegal
Togo
Tunisia
Western Sahara
For the purpose of this statistical exercise, the following countries have been considered as PART OF THE BRITISH EMPIRE for entire period up to 1945:
Botswana
Egypt
The Gambia
Ghana
Kenya
Lesotho
Malawi
Mauritius
Namibia ,
Nigeria
Seychelles,
Sierra Leone
Somalia
South Africa
St Helena
Sudan
Swaziland
Tanzania
Tristan da Cunha
Uganda
Zambia
Zimbabwe
[blue colour indicates those countries that were not part of British Empire for entire period]
2. List countries included in geographical region
[article ID:199]
List of African countries currently used on database:
Algeria
Angola
Ascension Island
Benin Republic
Botswana
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cameroon Cameroun
Cape Verde
Central African Republic
Chad
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of
Congo, People's Republic of
Côte d'Ivoire Ivory Coast
Djibouti
Egypt
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Ethiopia
Gabon
The Gambia
Ghana
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Ivory Coast Côte d'Ivoire
Kenya
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Madagascar
Malawi
Mali
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Melilla
Morocco
Mozambique (Moçambique)
Namibia
Niger
Nigeria
Reunion
Rwanda
São Tomé & Príncipe
Senegal
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Somalia
South Africa
St Helena
Sudan
Swaziland
Tanzania
Togo
Tristan da Cunha
Tunisia
Uganda
Western Sahara
Zambia
Zimbabwe
NB Madeira is counted geographically as part of Africa but culturally it is part of Europe (there was no indigenous population before the Portuguese colonised it) I have therefore included it within Portugal within the European statistics.
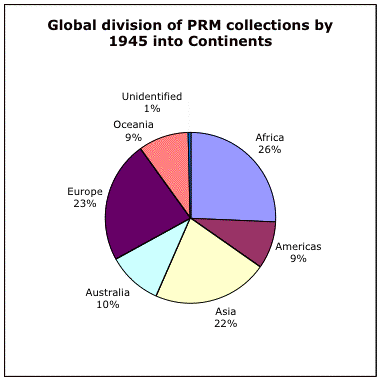
3. Total number of objects from geographical region
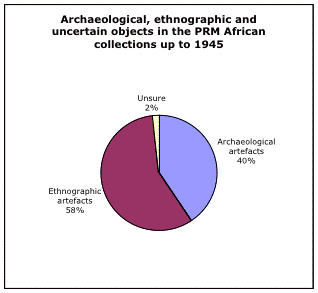
4. Total number of objects for geographical region divided into archaeological and ethnographic objects
[article ID:201]
Definitely ethnographic - 27,178
Definitely archaeological - 19,078
Possibly archaeological or ethnographic - 858
This is a very close match to the division globally (60 - 40).
Note that this includes 35 Madeiran entries that are otherwise excluded from the African statistics (they are also counted as European)
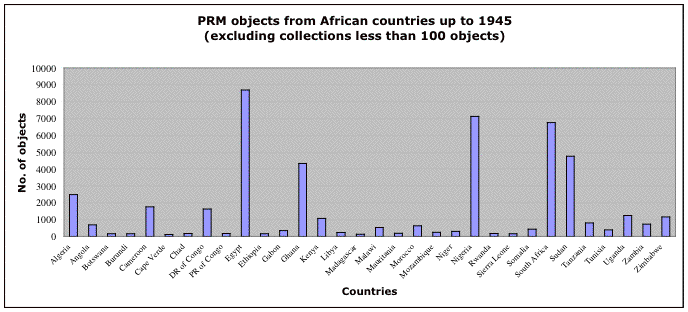
5. Total number of objects obtained from each country of region
[article ID:202]
Algeria - 2,480
Angola - 702
Ascension Island - 0 [from this point discounted as country in stats]
Benin Republic - 58
Botswana - 177
Burkina Faso - 19
Burundi - 173
Cameroon Cameroun - 1,756
Cape Verde - 133
Central African Republic - 36
Chad - 182
Comoros - 2
Congo, Democratic Republic of - 1,635
Congo, People's Republic of - 178
Côte d'Ivoire Ivory Coast - 19
Djibouti - 25
Egypt - 8,673
Equatorial Guinea - 19
Eritrea - 8
Ethiopia - 172
Gabon - 356
The Gambia - 55
Ghana - 4,331
Guinea - 18
Guinea-Bissau - 13
Kenya - 1,085
Lesotho - 22
Liberia - 30
Libya - 240
Madagascar - 147
Malawi - 546
Mali - 77
Mauritania - 193
Mauritius - 3
Mayotte - 0 [from this point discounted as country in stats]
Melilla - 0 [from this point discounted as country in stats]
Morocco - 635
Mozambique (Moçambique) - 259
Namibia - 53
Niger - 309
Nigeria - 7,119
Reunion - 0 [from this point discounted as country in stats]
Rwanda - 183
São Tomé & Príncipe - 0 [from this point discounted as country in stats]
Senegal - 31
Seychelles - 6
Sierra Leone - 167
Somalia - 436
South Africa - 6,747
St Helena - 0 [from this point discounted as country in stats]
Sudan - 4,754
Swaziland - 4
Tanzania - 814
Togo - 91
Tristan da Cunha St Helena - 0 [from this point discounted as country in stats]
Tunisia - 395
Uganda - 1,245
Western Sahara - 0 [from this point discounted as country in stats]
Zambia - 734
Zimbabwe - 1,170
NB there is double counting between the countries. Many objects are not clearly either Congo DR or PR so double counting is even more pronounced between these two countries
Note also that there are 2,132 objects for which no country has been identified, many of these are identified by loose regional associations such as West Africa etc. However I have not counted them in any of the statistics about countries or regions.
African countries with the most objects, up to 1945
Egypt - 8,673
Nigeria - 7,119
South Africa - 6,747
Sudan - 4,754
Ghana - 4,331
Algeria - 2,480
Cameroon Cameroun - 1,756
Congo, Democratic Republic of - 1,635
Uganda - 1,245
Zimbabwe - 1,170
Kenya - 1,085
Tanzania - 814
Zambia - 734
Angola - 702
Morocco - 635
Malawi - 546
Somalia - 436
Tunisia - 395
Gabon - 356
Niger - 309
Mozambique (Moçambique) - 259
Libya - 240
Mauritania - 193
Rwanda - 183
Chad - 182
Congo, People's Republic of - 178
Botswana - 177
Burundi - 173
Ethiopia - 172
Sierra Leone - 167
Madagascar - 147
Cape Verde - 133
Togo - 91
Mali - 77
Benin Republic - 58
The Gambia - 55
Namibia - 53
Central African Republic - 36
Senegal - 31
Liberia - 30
Djibouti - 25
Lesotho - 22
Burkina Faso - 19
Côte d'Ivoire Ivory Coast - 19
Equatorial Guinea - 19
Guinea - 18
Guinea-Bissau - 13
Eritrea - 8
Seychelles - 6
Swaziland - 4
Mauritius - 3
Comoros - 2
African countries with the most objects, up to 1945 with Colonial countries marked in blue
Egypt - 8,673
Nigeria - 7,119
South Africa - 6,747
Sudan - 4,754
Ghana - 4,331
Algeria - 2,480
Cameroon Cameroun - 1,756
Congo, Democratic Republic of - 1,635
Uganda - 1,245
Zimbabwe - 1,170
Kenya - 1,085
Tanzania - 814
Zambia - 734
Angola - 702
Morocco - 635
Malawi - 546
Somalia - 436
Tunisia - 395
Gabon - 356
Niger - 309
Mozambique (Moçambique) - 259
Libya - 240
Mauritania - 193
Rwanda - 183
Chad - 182
Congo, People's Republic of - 178
Botswana - 177
Burundi - 173
Ethiopia - 172
Sierra Leone - 167
Madagascar - 147
Cape Verde - 133
Togo - 91
Mali - 77
Benin Republic - 58
The Gambia - 55
Namibia - 53
Central African Republic - 36
Senegal - 31
Liberia - 30
Djibouti - 25
Lesotho - 22
Burkina Faso - 19
Côte d'Ivoire Ivory Coast - 19
Equatorial Guinea - 19
Guinea - 18
Guinea-Bissau - 13
Eritrea - 8
Seychelles - 6
Swaziland - 4
Mauritius - 3
Comoros - 2
Unsurprisingly lots of objects come from colonial areas. The non-colonial areas with the biggest collections in the top 20 for African countries are:
Algeria - 2,480
Cameroon Cameroun - 1,756
Congo, Democratic Republic of - 1,635
Angola - 702
Morocco - 635
Tunisia - 395
Gabon - 356
Niger - 309
There is a large single collection from Algeria which probably explains why that comes so high (Hilton-Simpson, roughly a quarter of the Algerian collection at 1945), and the same is true for Cameroon (Mervyn David Waldegrave Jeffreys, at 1,553, his is almost the entirety of the Cameroon collections by 1945). Nearly a quarter of the Democratic Republic of Congo's collections come from Emil Torday so yet again a single collector probably affects the overall figures.
The same story is true for Angola, where Antoinette Powell-Cotton gave 477 objects, well over half of the entire Angolan collection up to 1946. There does not seem to be a predominating collector of Moroccan and Tunisian objects, so it might be geographical proximity that explains their relatively high positions. Just under a third of the Gabon objects were collected by Robert Bruce Napoleon Walker and nearly 5/6ths of the Niger collections come from another single donor Francis James Rennell Rodd.
It therefore seems that single field collectors or large donations from an individual of objects from a single country can affect the figures quite considerably.
Note that there are several British colonies from whom we have no objects:
Ascension Island
St Helena and Tristan da Cunha
Although the easy explanation for this is that the population of these places is very low (and therefore presumably their material culture).
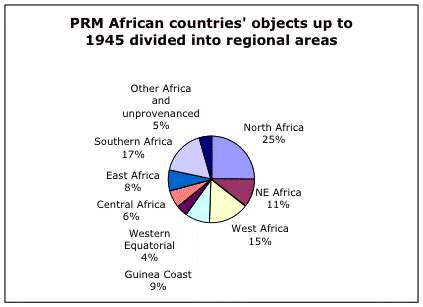
Regional breakdown of African figures
[article ID:203]
We have used the divisions based upon the 'Dictionary of Art' divisions: They are defined as follows, where countries in bold type and underlined were countries (either whole or part thereof) under British control at some point in the period 1880-1900, and countries in bold only were also under British control but not in 1880-1900:
North Africa Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco (incl. Western Sahara), Mauritania
Northeast Africa Sudan, Somalia, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti
West Africa Nigeria, The Gambia, Niger, Mali, Burkina Faso, Senegal, Chad
Guinea Coast Ghana, Sierra Leone, Togo, Guinea-Bissau, Benin Republic, Guinea,
Liberia, Cote d Ivoire
Western Equatoria Cameroon, Central African Republic, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea
Central Africa Zambia, DR of Congo, PR of Congo, Angola (incl. Cabinda)
East Africa Kenya, Uganda, Malawi, Zanzibar/Tanzania, Rwanda, Burundi
Southern Africa Zimbabwe, Botswana, South Africa, Lesotho, Swaziland, Mozambique,
Namibia
Other Mauritius, Comoros Islands, Cape Verde, Madagascar [plus Seychelles, Ascension Island, Tristan da Cunha, St Helena, etc]
North Africa:
Egypt - 8,673
Libya - 240
Tunisia - 395
Algeria - 2,480
Morocco - 635
Mauritania - 193
Total of North African objects up to 1945: 12,616
Northeast Africa:
Sudan - 4,754
Somalia - 436
Eritrea - 8
Ethiopia - 172
Djibouti - 25
Total of NE African objects up to 1945: 5,395
West Africa:
Nigeria - 7,119
The Gambia - 55
Niger - 309
Mali - 77
Burkina Faso - 19
Senegal - 31
Chad - 182
Total of West African objects up to 1945: 7,792
Guinea Coast:
Ghana - 4,331
Sierra Leone - 167
Togo - 91
Guinea-Bissau - 13
Benin Republic - 58
Guinea - 18
Liberia - 30
Côte d'Ivoire Ivory Coast - 19
Total of Guinea Coast objects up to 1945: 4,727
Western Equatorial:
Cameroon Cameroun - 1,756
Central African Republic - 36
Gabon - 356
Equatorial Guinea - 19
Total of Western Equatorial objects up to 1945: 2,167
Central Africa:
Zambia - 734
Congo, Democratic Republic of - 1,635
Congo, People's Republic of - 178
Angola - 702
Total of Central African objects up to 1945: 3,249
East Africa:
Kenya - 1,085
Uganda - 1,245
Malawi - 546
Tanzania - 814
Rwanda - 183
Burundi - 173
Total of East African objects up to 1945: 4,046
Southern Africa:
Zimbabwe - 1,170
Botswana - 177
South Africa - 6,747
Lesotho - 22
Swaziland - 4
Mozambique (Moçambique) - 259
Namibia - 53
Total of Southern African objects up to 1945: 8,432
Other Africa and unprovenanced:
Mauritius - 3
Comoros - 2
Cape Verde - 133
Madagascar - 147
Seychelles - 6
Total for Other Africa objects up to 1945: 291 + 2133 [those countries not given specific country or countries provenance ] = 2423
Note also that there are 2132 objects for which no country has been identified, many of these are identified by loose regional associations such as West Africa etc. However we have not counted them in any of the statistics about countries or regions apart from this one
North African objects up to 1945: 12,616
NE African objects up to 1945: 5,392
West African objects up to 1945: 7792
Guinea Coast objects up to 1945: 4727
Western Equatorial objects up to 1945: 2167
Central African objects up to 1945: 3249
East African objects up to 1945: 4046
Southern African objects up to 1945: 8432
Other African objects up to 1945: 2424
Because of the double counting between countries of one object (because it is not accurately enough provenanced by the original documentation) caution must be taken when examining statistics such as this however it does appear that North African objects form roughly a quarter of the entire African collections up to 1945, with West Africa and Southern Africa being next best represented.
Overall division of African objects into those that came from parts of the British Empire and those that did not:
Botswana - 177
Egypt - 8,673
The Gambia - 55
Ghana - 4,331
Kenya - 1085
Lesotho - 22
Malawi - 546
Mauritius - 3
Namibia - 53
Nigeria - 7,119
Seychelles - 6
Sierra Leone - 167
Somalia - 436
South Africa - 6,747
Sudan - 4,754
Swaziland - 4
Tanzania - 814
Uganda - 1,245
Zambia - 734
Zimbabwe - 1,170
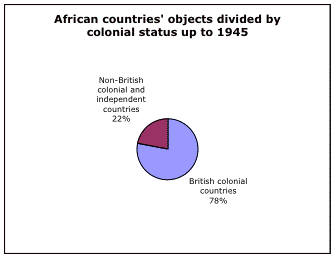
Total for objects from African countries that were part of British Empire up to 1945: 38,141*
[ * Double counting between countries, some of which may be inside the British Empire and some outside will account for the total of colonial and non-colonial countries exceeding the total count of objects!]
Non British Empire countries' objects:
Algeria - 2,480
Angola - 702
Benin Republic - 58
Burkina Faso - 19
Burundi - 173
Cameroon Cameroun - 1,756
Cape Verde - 133
Central African Republic - 36
Chad - 182
Comoros - 2
Congo, Democratic Republic of - 1,635
Congo, People's Republic of - 178
Côte d'Ivoire Ivory Coast - 19
Djibouti - 25
Equatorial Guinea - 19
Eritrea - 8
Ethiopia - 172
Gabon - 356
Guinea - 18
Guinea-Bissau - 13
Liberia - 30
Libya - 240
Madagascar - 147
Mali - 77
Mauritania - 193
Morocco - 635
Mozambique (Moçambique) - 259
Niger - 309
Rwanda - 183
Senegal - 31
Togo - 91
Tunisia - 395
Total for objects from outside the British Empire in Africa up to 1945: 10,574*
[ * Double counting between countries, some of which may be inside the British Empire and some outside will account for the total of colonial and non-colonial countries exceeding the total count of objects]
Part of Cameroon was British for the relevant period BUT it was a relatively small part, as the northern part of British Cameroon joined Nigeria, only the southern part became part of the Republic of Cameroon. We have therefore decided to exclude the whole country, the majority of which was for most of the relevant period part of the French Empire.
Was British from 1941, but such a short period that difficult to access statistically (We would have to be sure that the object had been COLLECTED prior to 1941)
Togo was originally German and from 1914 was shared between the British and French although it does not appear to have been a very important British colony (the French part pre-dominating). We have therefore decided to consider the whole NOT a British colony despite the fact that part was for over half the colonial period (this also reflects the practical implications that it is extremely unlikely that we can provenance objects well enough to know if they come from French or British Togoland).
Egypt was never a formal colony as such but can be considered to be so for the purposes of this exercise
Namibia was part of South Africa (and therefore for the purposes of this exercise part of British Empire) from 1919, before that date it was German: it may not be possible to divide the object neatly to being collected before and after this date
NB Namibia not included as part of British Empire in Sandra's pilot project, the position post 1900 changes
The Seychelles formally became a British crown colony in 1903 and was declared independent in 1976
NB Seychelles not included as part of British Empire in Sandra's pilot project, the position post 1900 changes
Note that part of Somalia was for a time part of Italy but it will not be possible to identify the provenance of most (?all) objects so precisely that it will be possible to identify which these are so for these purposes it has all been considered part of British Empire.
South Africa was technically a protectorate rather than a colony for most of the relevant period, however in effect it was part of the British Empire
Again was not incorporated into what became South Africa until 1894 but it is probably too difficult (?impossible) to sort out those items which came into the collections prior to 1894
Tanzania was German until 1919
Uganda was formally part of British Empire from 1894